流程
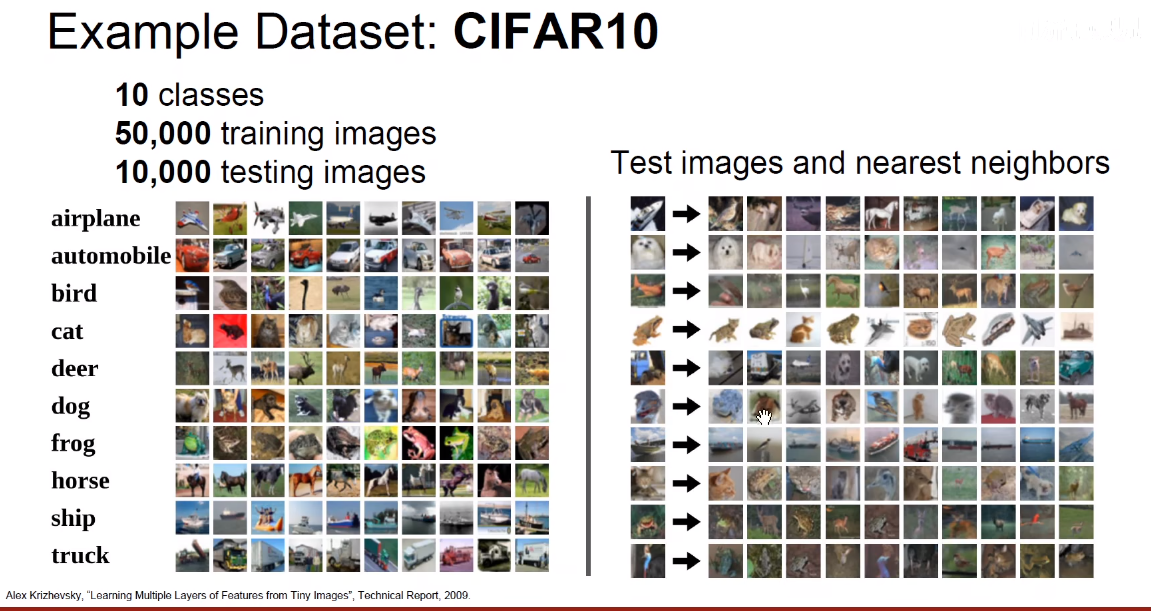
图像分割:计算机视觉的核心问题。
一张图片是由多个RBG构成的数组,但是对于计算机视觉来说,摄像机在不同的角度观测会带来截然不同的像素矩阵。

图像分类:
- 输入:图像
- 输出:分类
- 难点:没有硬编码的解决方案
- 思路:使用数据驱动,灌输大量的图片及其标签,在其上训练一个分类器,对其打分。
KNN
最近邻
找到最相似的图片,按最近的标签来。
最近邻的python2实现:
import numpy as np
class NearestNeighbor(object):
def __init__(self):
pass
def train(self, X, y):
""" X is N x D where each row is an example. Y is 1-dimension of size N """
# the nearest neighbor classifier simply remembers all the training data
self.Xtr = X
self.ytr = y
def predict(self, X):
""" X is N x D where each row is an example we wish to predict label for """
num_test = X.shape[0]
# lets make sure that the output type matches the input type
Ypred = np.zeros(num_test, dtype = self.ytr.dtype)
# loop over all test rows
for i in range(num_test):
# find the nearest training image to the i'th test image
# using the L1 distance (sum of absolute value differences)
distances = np.sum(np.abs(self.Xtr - X[i,:]), axis = 1)
min_index = np.argmin(distances) # get the index with smallest distance
Ypred[i] = self.ytr[min_index] # predict the label of the nearest example
return Ypred训练时间:
测试时间:
但是我们宁愿训练时间长一点,但是测试时间短。
决策边界:垂直平分线
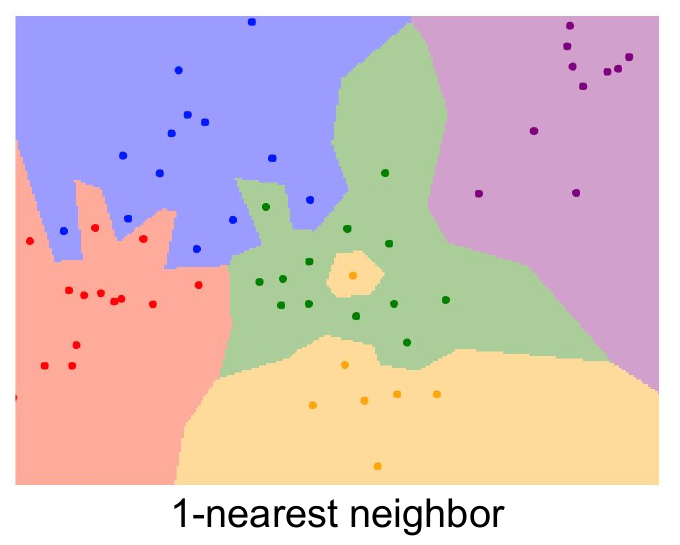
这个边界不够优秀,因为其包含了一些噪声点。
K-最近邻(KNN)
让最亲密的点投票。
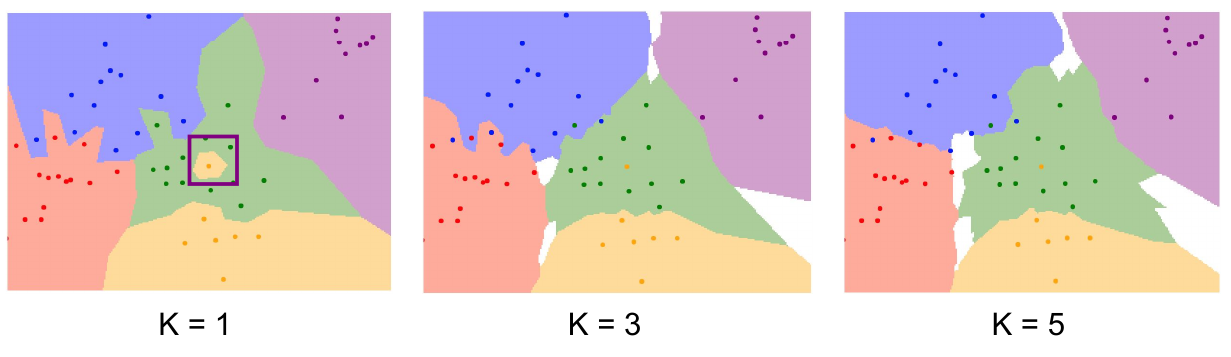
超参数:
- 最近邻个数k:
k=1:只做模拟题- 留一部分测试,只做模拟题但不对答案
- 一边写一边看答案
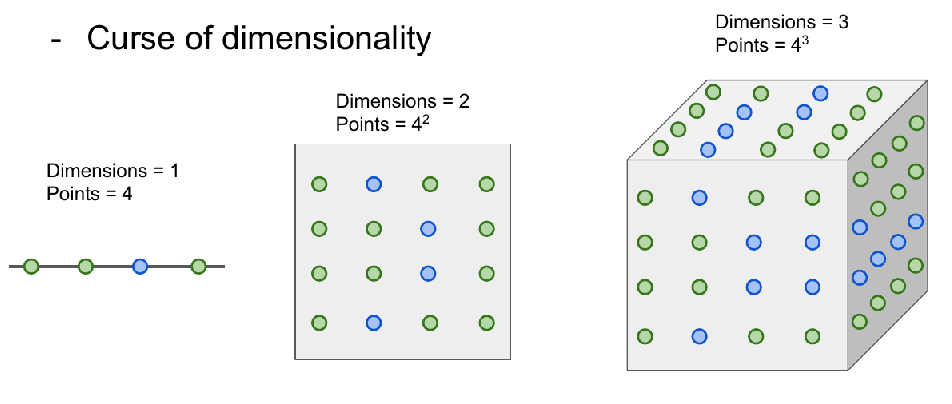
维度诅咒
k越多,那么计算量越大,可能根本算不完。
总结:kNN 的实际应用
如果您希望在实践中应用 kNN(希望不是在图像上,或者可能仅作为基线),请按以下步骤操作:
- 预处理数据:将数据中的特征(例如图像中的一个像素)标准化,使其均值和单位方差为零。我们将在后面的部分中更详细地介绍这一点,并选择在本节中不介绍数据归一化,因为图像中的像素通常是同质的并且不会表现出广泛不同的分布,从而减轻了数据归一化的需要。
- 如果您的数据维度非常高,请考虑使用降维技术,例如 PCA(wiki 参考、CS229ref、博客参考)、NCA(wiki 参考、博客参考),甚至是随机投影。
- 将训练数据随机分割为训练/验证数据。根据经验,70-90% 的数据通常会进入训练集。此设置取决于您拥有多少个超参数以及您期望它们具有多大的影响力。如果有许多超参数需要估计,您应该宁可使用更大的验证集来有效地估计它们。如果您担心验证数据的大小,最好将训练数据分成几部分并执行交叉验证。如果您能负担得起计算预算,那么交叉验证总是更安全(折叠越多越好,但更昂贵)。
- 在验证数据上训练和评估 kNN 分类器(对于所有折叠,如果进行交叉验证),针对k的多种选择(例如,越多越好)并跨越不同的距离类型(L1 和 L2 是很好的候选者)
- 如果您的 kNN 分类器运行时间过长,请考虑使用近似最近邻库(例如FLANN)来加速检索(以一定的准确性为代价)。
- 记下提供最佳结果的超参数。存在一个问题,您是否应该使用具有最佳超参数的完整训练集,因为如果您要将验证数据折叠到训练集中,最佳超参数可能会发生变化(因为数据的大小会更大)。实际上,在最终分类器中不使用验证数据并考虑在估计超参数时将其*烧毁会更干净。*评估测试集上的最佳模型。报告测试集的准确性并将结果声明为 kNN 分类器在您的数据上的性能。
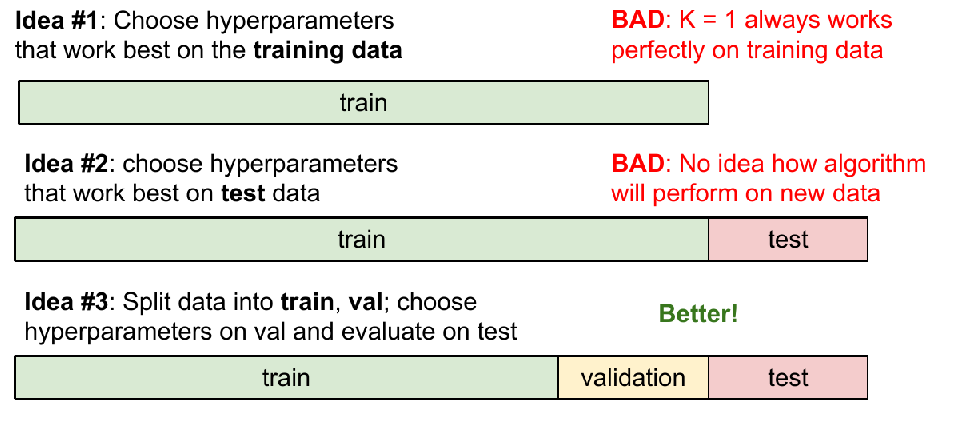
交叉验证
将训练用题库划分成几分,然后测试,最后平均一下。
L1距离
曼哈顿很多高楼大厦,只能顺着街道走,不管怎么走,距离都是定值:横纵距离之差。

L2距离
也叫欧几里得距离
不管怎么旋转图像,都不会改变距离的值。

这四张有不同的L2距离,但其实有相同的特点。
线性分类器
代数方面
用一根“直线”将样本分类成两份。是神经网络的第一个处理模块。
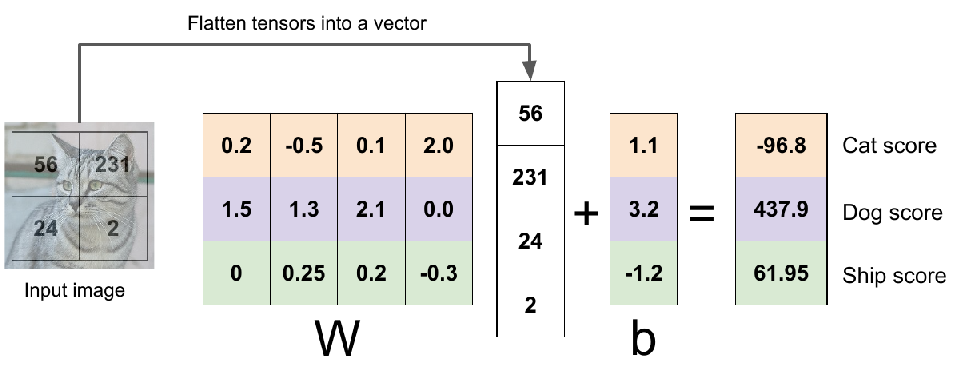
拓展到图像层面,就是对每个像素进行线性分类,最后得到不同类别的对应分数,从其中找一个最大的结果就是分类。
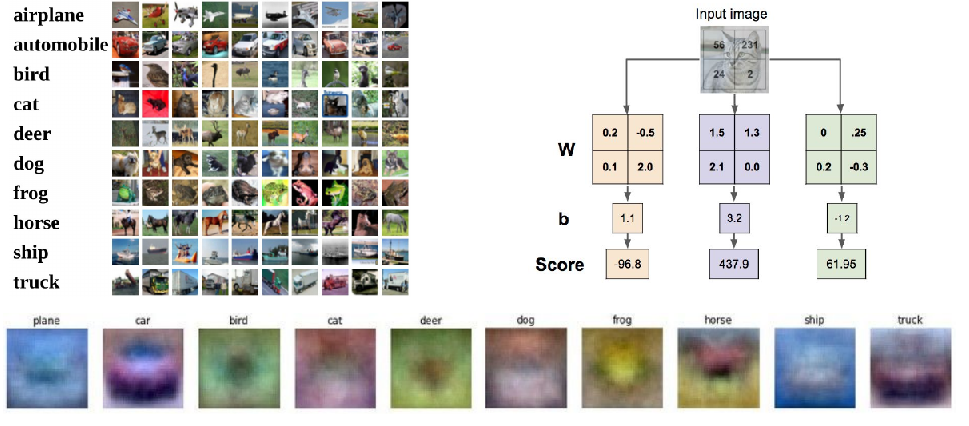
可视化方面
这里将计算得到的b图像打印出来了:看起来和原图有点像
几何方面
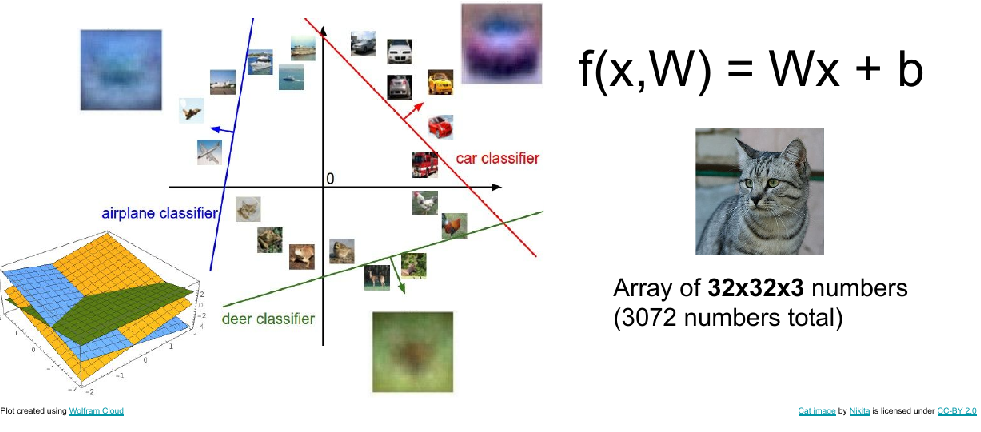
在n维空间中的超平面将数据分类
问题
比较直,不会拐弯,不能解决xor、圆形、多个峰值的问题。
代码
def L_i(x, y, W):
"""
unvectorized version. Compute the multiclass svm loss for a single example (x,y)
- x is a column vector representing an image (e.g. 3073 x 1 in CIFAR-10)
with an appended bias dimension in the 3073-rd position (i.e. bias trick)
- y is an integer giving index of correct class (e.g. between 0 and 9 in CIFAR-10)
- W is the weight matrix (e.g. 10 x 3073 in CIFAR-10)
"""
delta = 1.0 # see notes about delta later in this section
scores = W.dot(x) # scores becomes of size 10 x 1, the scores for each class
correct_class_score = scores[y]
D = W.shape[0] # number of classes, e.g. 10
loss_i = 0.0
for j in range(D): # iterate over all wrong classes
if j == y:
# skip for the true class to only loop over incorrect classes
continue
# accumulate loss for the i-th example
loss_i += max(0, scores[j] - correct_class_score + delta)
return loss_i
def L_i_vectorized(x, y, W):
"""
A faster half-vectorized implementation. half-vectorized
refers to the fact that for a single example the implementation contains
no for loops, but there is still one loop over the examples (outside this function)
"""
delta = 1.0
scores = W.dot(x)
# compute the margins for all classes in one vector operation
margins = np.maximum(0, scores - scores[y] + delta)
# on y-th position scores[y] - scores[y] canceled and gave delta. We want
# to ignore the y-th position and only consider margin on max wrong class
margins[y] = 0
loss_i = np.sum(margins)
return loss_i
def L(X, y, W):
"""
fully-vectorized implementation :
- X holds all the training examples as columns (e.g. 3073 x 50,000 in CIFAR-10)
- y is array of integers specifying correct class (e.g. 50,000-D array)
- W are weights (e.g. 10 x 3073)
"""
# evaluate loss over all examples in X without using any for loops
# left as exercise to reader in the assignment