软硬连接文件计数
2009年考研题
Question
Answer
使用ln命令验证
- 创建一个文件,例如
file1.txt:
echo "This is a test file." > file1.txt- 创建软链接和硬链接:
使用 -s 参数创建软链接:
ln -s file1.txt file2_softlink.txt使用不带 -s 参数创建硬链接:
ln file1.txt file3_hardlink.txt- 查看文件的链接计数:
ls -l file1.txt file2_softlink.txt file3_hardlink.txt输出结果将显示类似于以下内容:
-rw-r--r-- 2 root root 21 Dec 5 16:54 file1.txt
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Dec 5 16:55 file2_softlink.txt -> file1.txt
-rw-r--r-- 2 root root 21 Dec 5 16:54 file3_hardlink.txt
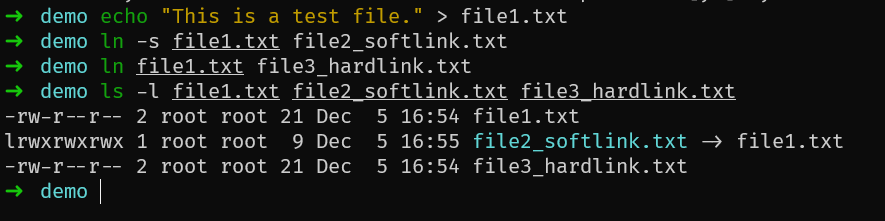
在这个示例中,你会看到 file1.txt 和 file3_hardlink.txt 的链接计数都是 2,因为它们是同一个文件的硬链接。而 file2_softlink.txt 是软链接,它的链接计数是 1。
接下来,你可以删除 file1.txt 文件并查看链接计数的变化:
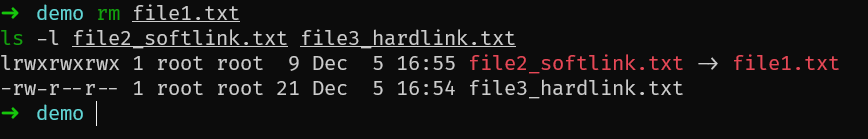
rm file1.txt
ls -l file2_softlink.txt file3_hardlink.txt删除了 file1.txt 后,你会发现 file2_softlink.txt 的链接计数仍然是 1,而 file3_hardlink.txt 的链接计数也是 1。这是因为硬链接在原始文件被删除后仍然指向原始文件的数据块。
那么这时能访问 file2和 file3 中的谁呢?
$ cat file2_softlink.txt
cat: file2_softlink.txt: No such file or directory
$ cat file3_hardlink.txt
This is a test file.发现f2不能访问但f3能访问
硬链接的读写指针位置一样吗
2017年考研题
Question
Answer
当时 I 没细看就过去了,但还是决定实验一下
代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
const char* filename = "file.txt";
const char* text = "Hello, this is a test file for hard links.";
int fd;
// 创建文件并写入数据
fd = open(filename, O_CREAT | O_RDWR, 0644);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("Error opening file");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (write(fd, text, strlen(text)) == -1) {
perror("Error writing to file");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 创建硬链接
if (link(filename, "file_link") == -1) {
perror("Error creating hard link");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 创建子进程
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
perror("Error forking");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
} else if (pid == 0) { // 子进程
off_t offset_child;
// 子进程移动文件描述符的读写指针
offset_child = lseek(fd, 10, SEEK_SET);
if (offset_child == -1) {
perror("Error seeking in file (child)");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 获取并打印文件描述符的偏移量(子进程)
off_t current_offset_child = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_CUR);
printf("Child process - Offset in file: %lld\n", (long long)current_offset_child);
// 关闭文件描述符
close(fd);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
} else { // 父进程
off_t offset_parent;
// 父进程移动文件描述符的读写指针
offset_parent = lseek(fd, 20, SEEK_SET);
if (offset_parent == -1) {
perror("Error seeking in file (parent)");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 获取并打印文件描述符的偏移量(父进程)
off_t current_offset_parent = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_CUR);
printf("Parent process - Offset in file: %lld\n", (long long)current_offset_parent);
// 关闭文件描述符
close(fd);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
return 0;
}
输出:
$ ./a.out
Parent process - Offset in file: 20
Child process - Offset in file: 10
说明读写指针的位置确实不同



