资源获取就是初始化:Resource Acquisition Is Initialization
让对象的生命周期对应资源的生命周期,在 RAII 中,资源的获取是在对象构造时完成的,而资源的释放则是在对象析构时完成的。这种方式可以确保资源在任何情况下都能被正确地释放,包括正常的程序流程、异常的抛出等情况。
smart_pointer
构造就是申请,析构就是释放
- unique_ptr
- shared_ptr
- weak_ptr
- RefBase
lock_guard
对锁进行管理,自动加锁。
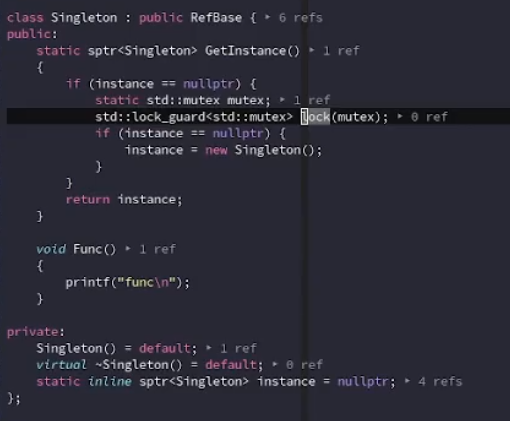
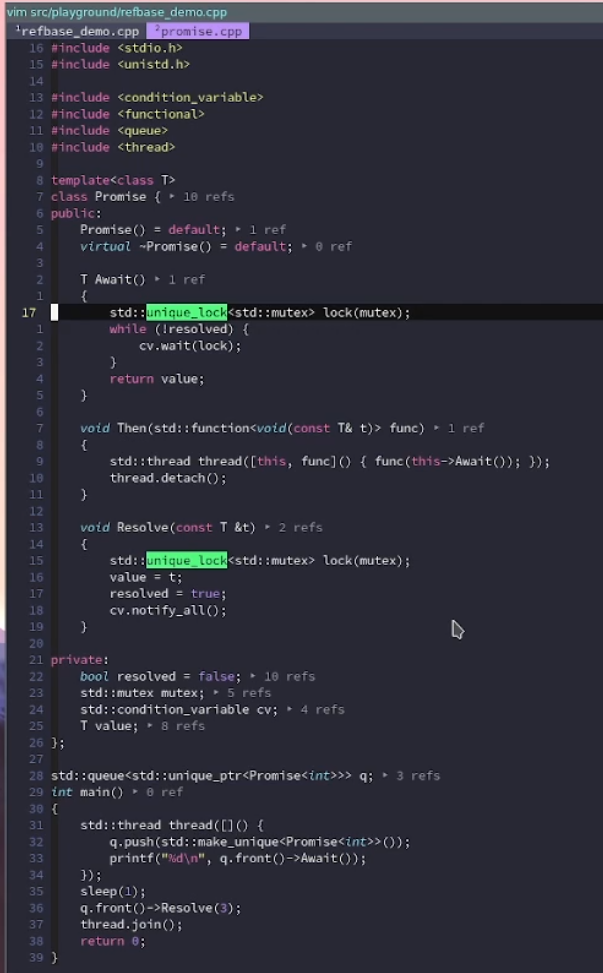
unique_lock
信号量:
file_guard
stl不提供,看名字是对文件的看守
#pragma once
// file_guard.h
class FileGuard {
public:
FileGuard(const char* filename, int flag);
~FileGuard();
bool IsOK() const; // 是不是打开成功了
int GetFD(); // 获取文件描述符
};#include "file_guard.h"
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// 构造函数,打开文件
FileGuard::FileGuard(const char* filename, int flag) {
fd = open(filename, flag);
if(IsOK() == false){
// printf("open: %s\n", stderror(errno));
}
}
// 析构函数,关闭文件
FileGuard::~FileGuard() {
if (fd != -1) {
close(fd);
}
}
// 检查文件是否打开成功
bool FileGuard::IsOK() const {
return fd != -1;
}
// 获取文件描述符
int FileGuard::GetFD() {
return fd;
}int main() {
FileGuard* f("/proc/self/exe", O_RDONLY);
if(!file.IsOK()) return false;
char str[8];
read(file.GetFD(), str, 7);
printf("%s\n", str);
return 0;
}mmap_guard
管理内存映射
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
// mmap_guard.h
class MmapGuard {
public:
MmapGuard(const char* filename, size_t length);
~MmapGuard();
void* GetAddr() const; // 获取映射的内存地址
bool IsOK() const; // 检查映射是否成功
private:
void* addr;
size_t length;
bool is_ok;
};
// mmap_guard.cpp
MmapGuard::MmapGuard(const char* filename, size_t length) : length(length), is_ok(false) {
int fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1) {
addr = MAP_FAILED;
} else {
addr = mmap(NULL, length, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE, fd, 0);
if (addr != MAP_FAILED) {
is_ok = true;
}
close(fd);
}
}
MmapGuard::~MmapGuard() {
if (is_ok) {
munmap(addr, length);
}
}
void* MmapGuard::GetAddr() const {
return addr;
}
bool MmapGuard::IsOK() const {
return is_ok;
}