算法原理
如果以 表示从起点到任意顶点 的实际距离, 表示任意顶点 到目标顶点的估算距离(根据所采用的评估函数的不同而变化),那么A*算法的估算函数为:
这个公式遵循以下特性:
- 如果 为0,即只计算任意顶点 到目标的评估函数 ,而不计算起点到顶点 的距离,则算法转化为使用贪心的搜索
- 如果 不大于顶点 到目标顶点的实际距离,则一定可以求出最优解,而且 越小,需要计算的节点越多,算法效率越低,常见的评估函数有——欧几里得距离、曼哈顿距离、切比雪夫距离;
- 如果 为0,即只需求出起点到任意顶点 的最短路径 ,而不计算任何评估函数 ,则转化为最短路问题,即Dijkstra算法,此时需要计算最多的顶点;
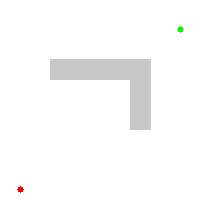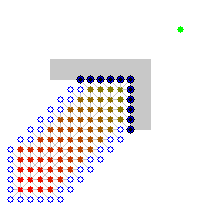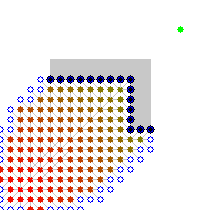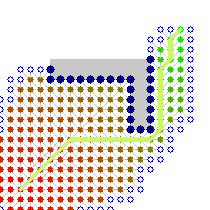
代码实现
# 预估代价
def heuristic(a: GridLocation, b: GridLocation) -> float:
(x1, y1) = a
(x2, y2) = b
return abs(x1 - x2) + abs(y1 - y2)
def a_star_search(graph: WeightedGraph, start: Location, goal: Location):
frontier = PriorityQueue()
frontier.put(start, 0)
came_from: dict[Location, Optional[Location]] = {}
cost_so_far: dict[Location, float] = {}
came_from[start] = None
cost_so_far[start] = 0
while not frontier.empty():
current: Location = frontier.get()
if current == goal:
break
for next in graph.neighbors(current):
new_cost = cost_so_far[current] + graph.cost(current, next)
if next not in cost_so_far or new_cost < cost_so_far[next]:
cost_so_far[next] = new_cost
priority = new_cost + heuristic(next, goal) # 每次使用代价最小的
frontier.put(next, priority)
came_from[next] = current
return came_from, cost_so_far